Prolonged inflammatory stimulation of fibroblasts promotes the formation of type III collagen and fibronectin in response to TGF-β1
Introduction
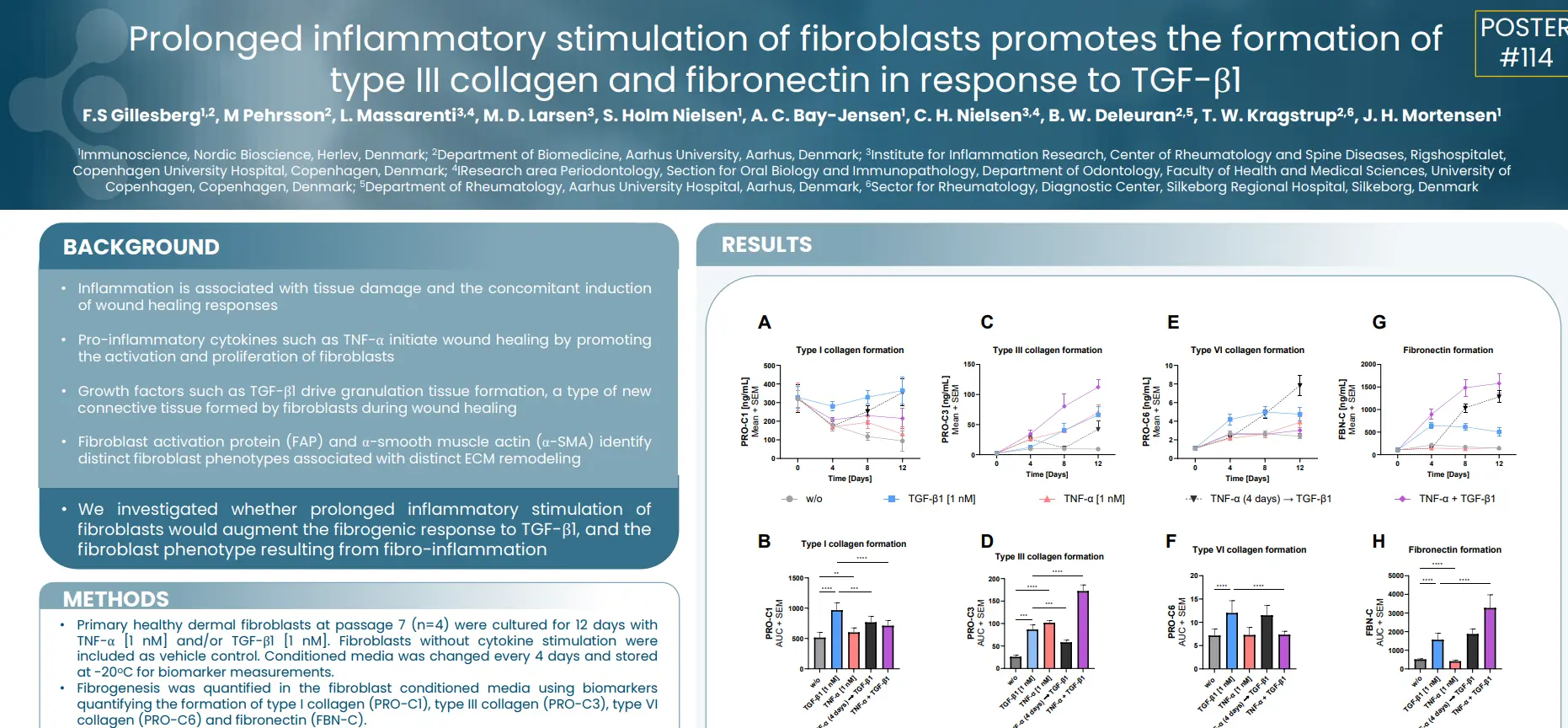
Inflammation is associated with tissue damage and the concomitant induction of wound healing responses. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α initiate wound healing by promoting the activation and proliferation of fibroblasts. Growth factors such as TGF-β1 drive granulation tissue formation, a type of new connective tissue formed by fibroblasts during wound healing. Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) identify distinct fibroblast phenotypes associated with distinct ECM remodeling.
In this study we investigated whether prolonged inflammatory stimulation of fibroblasts would augment the fibrogenic response to TGF-β1, and the fibroblast phenotype resulting from fibro-inflammation.
Poster
Conclusion
TNF-α shifts TGF-β1 stimulated α-SMA+ fibroblasts towards a fibro-inflammatory FAP+ phenotype. The TGF-β1 + TNF-α stimulation is characterized by increased type III collagen and fibronectin formation, while type I and VI collagen are reduced, compared to TGF-β1 stimulation only. In conclusion, the soluble nordicPRO-C3™ and FBN-C biomarkers may be used to identify FAP + fibroblast activity, associated with fibrogenesis.