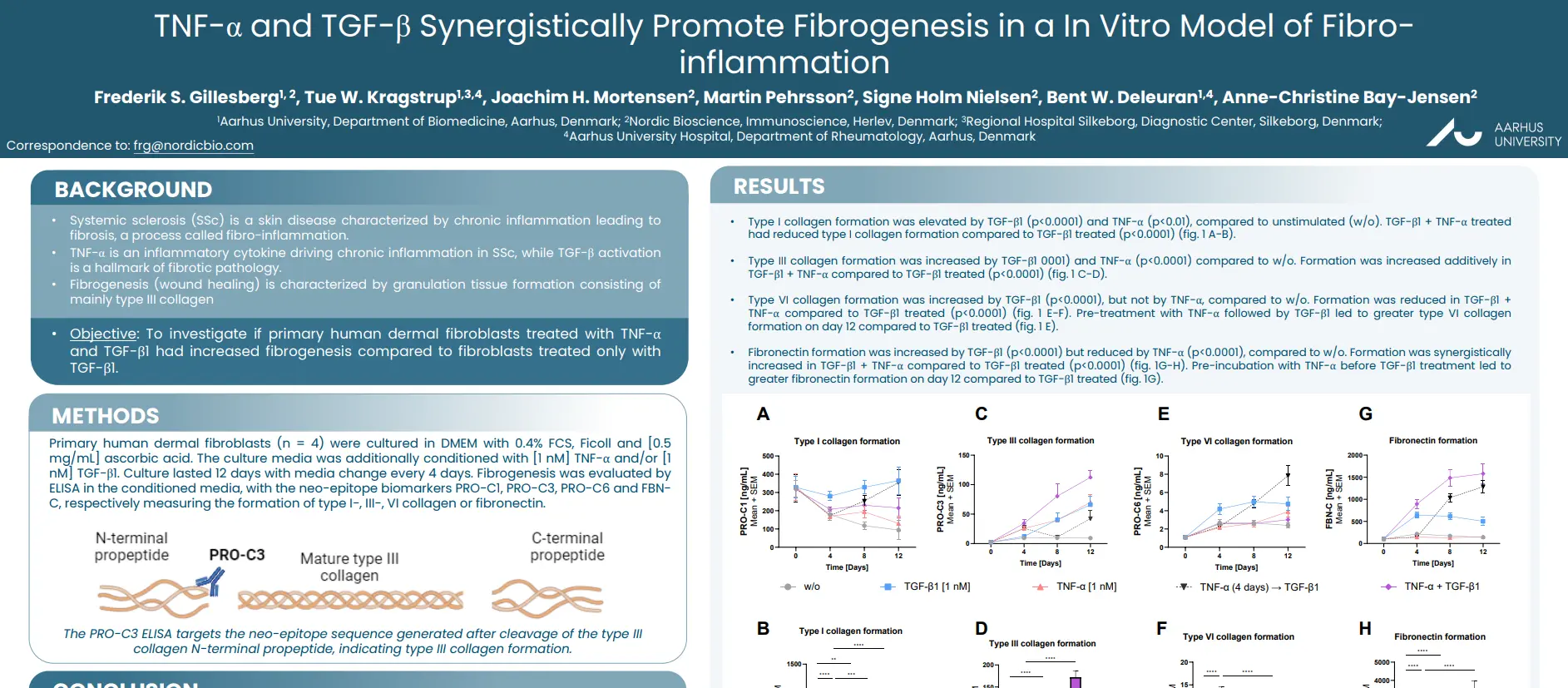
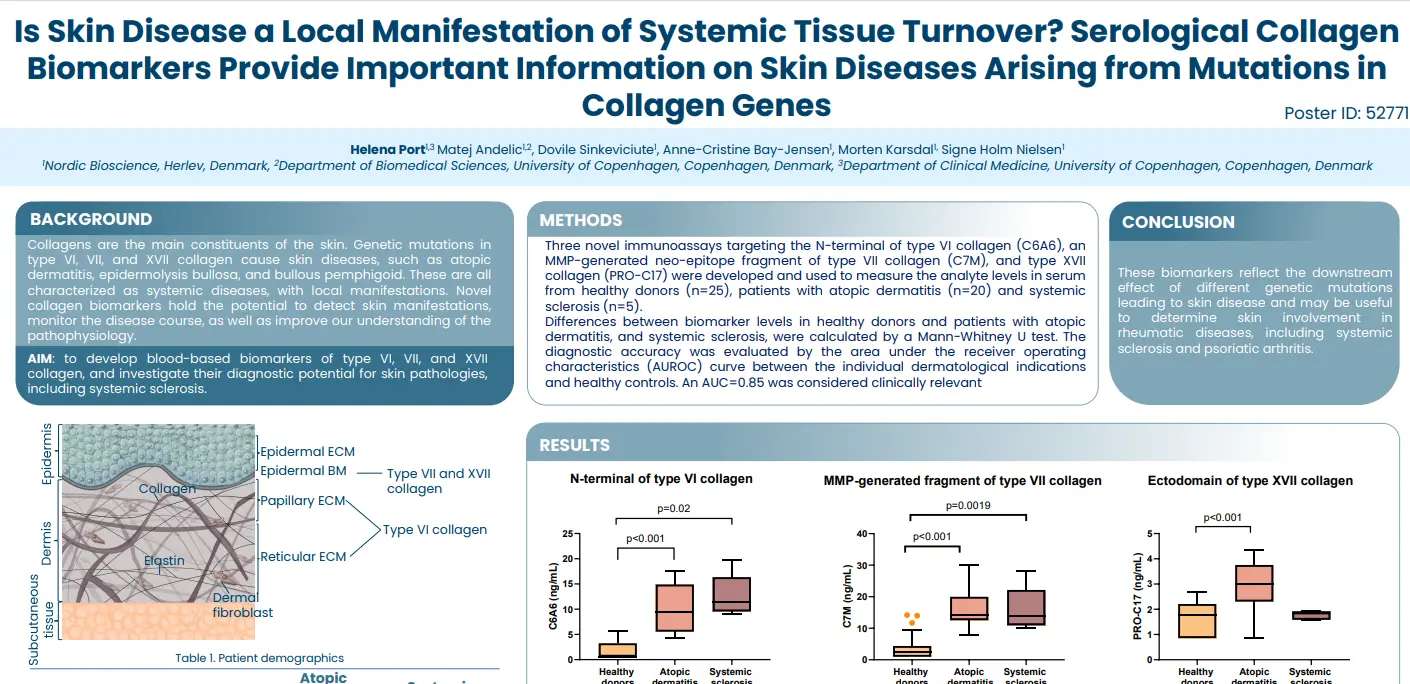
Novel tissue turnover biomarkers are associated with prolonged QTc and pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with systemic sclerosis
Introduction
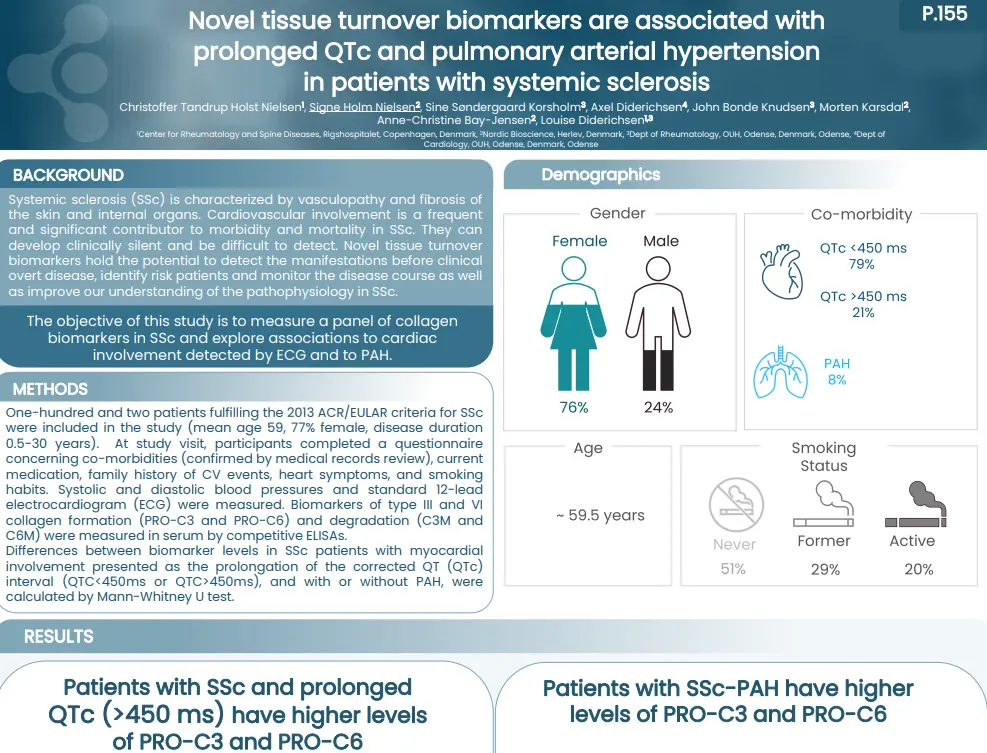
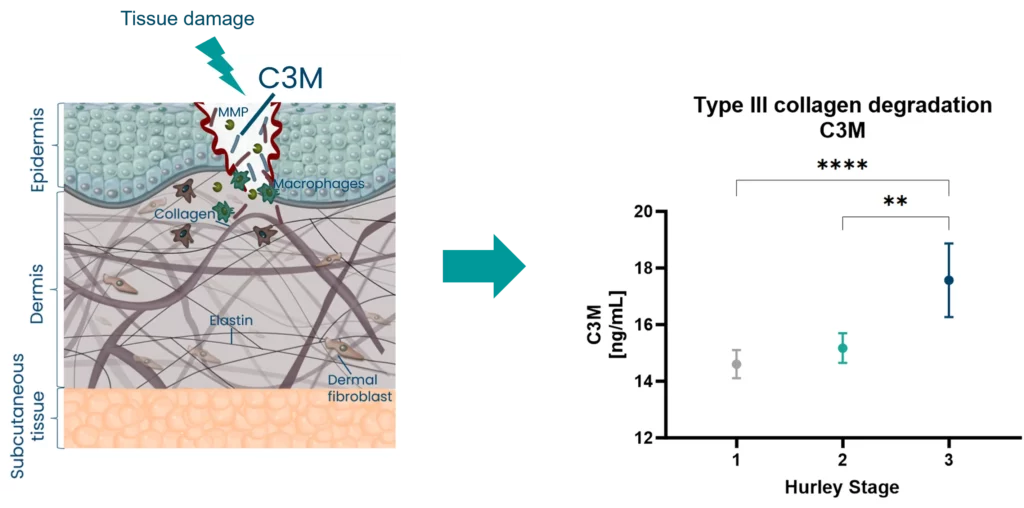
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterized by vasculopathy and fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. Cardiovascular involvement is a frequent and significant contributor to morbidity and mortality in SSc. They can develop clinically silent and be difficult to detect. Novel tissue turnover biomarkers hold the potential to detect the manifestations before clinical overt disease, identify risk patients and monitor the disease course as well as improve our understanding of the pathophysiology in SSc.
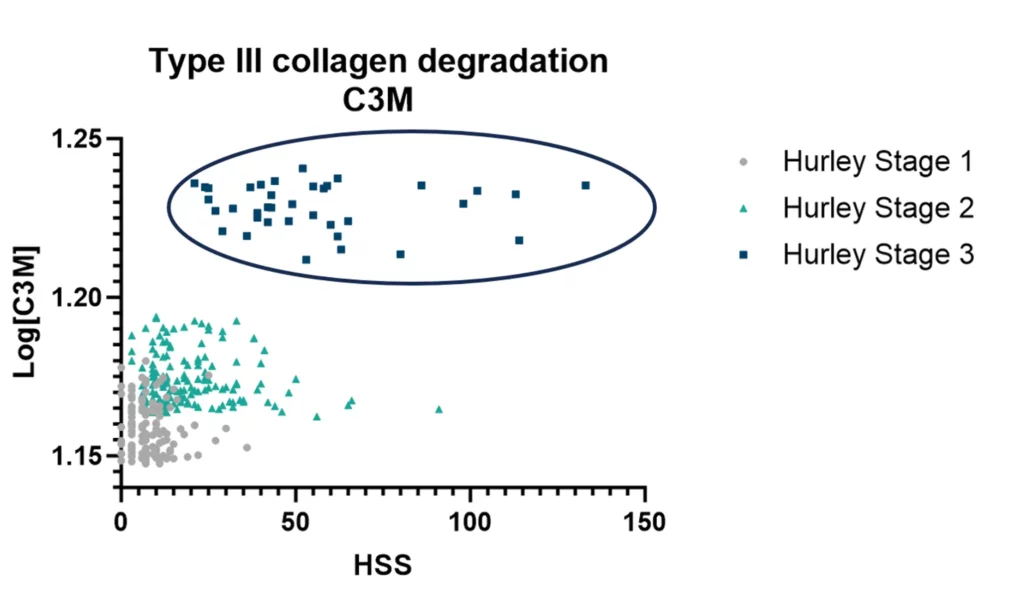
The objective of this study is to measure a panel of collagen biomarkers in SSc and explore associations to cardiac involvement detected by ECG and to PAH.
Poster
Conclusion
Patients with SSc and prolonged ECG presented an altered tissue turnover, by an increased level of nordicPRO-C3™ and nordicPRO-C6™. In addition, SSc patients with presence of PAH had increased levels of nordicPRO-C3™ and nordicPRO-C6™ as well. presented an altered tissue turnover in presence of PAH, and with a QTc>450 ms. Our study indicates that they could serve as biomarkers of these manifestations and warrant further studies in cardiac disease in SSc.