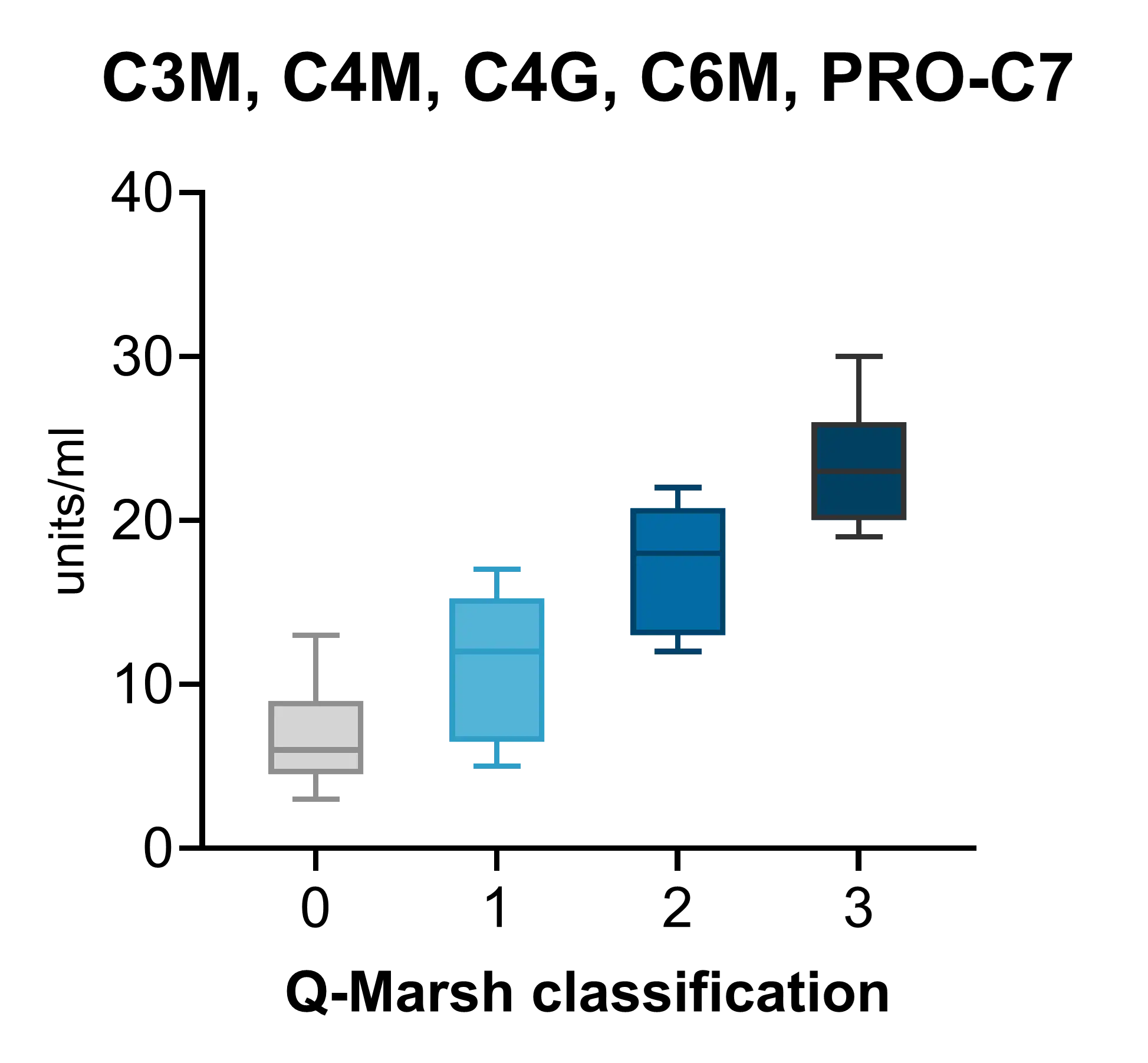
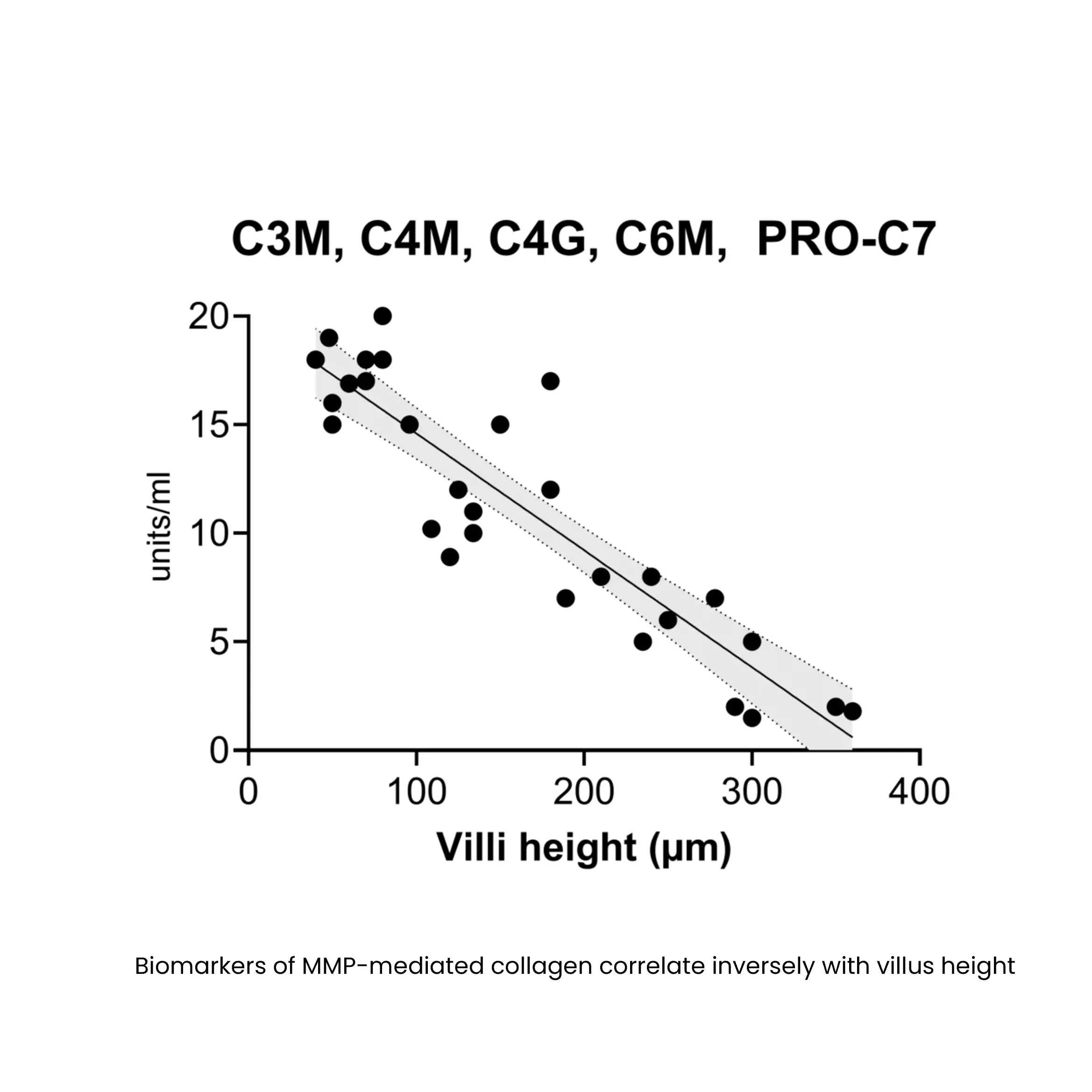
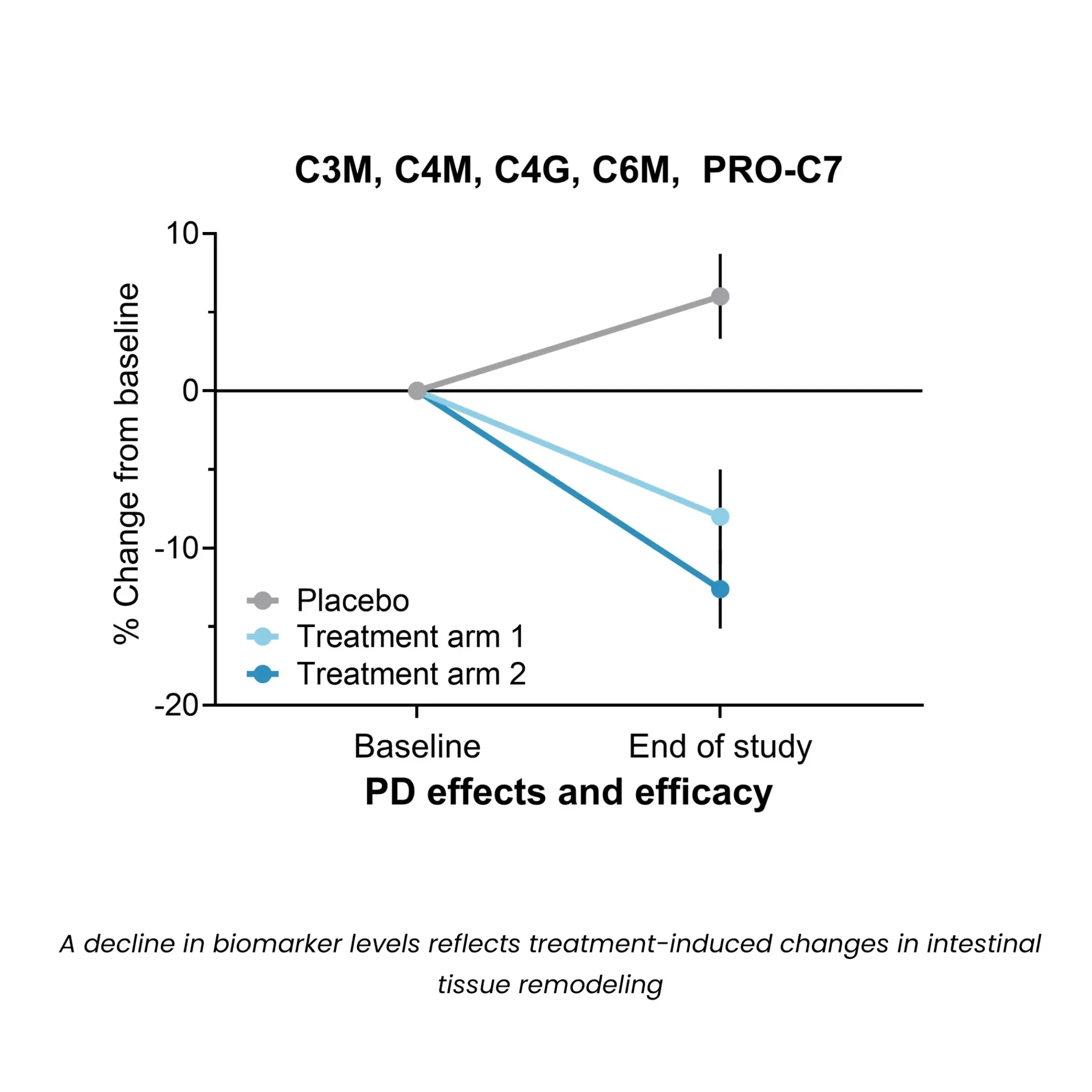
Celiac disease leads to inflammation and damage to the intestinal lining upon interaction with immunogenic gluten peptides, impacting tissue architecture and therefore directly altering the extracellular matrix (ECM).
Biomarkers of MMP-mediated collagen degradation (C3M, C4M, C6M) and immune cell activity (C4G) offer insights into epithelial integrity and the extent of tissue damage. By capturing real-time changes in tissue architecture, these biomarkers enable a more precise assessment of disease activity, therapeutic response, and pharmacodynamic effects, optimizing drug development and supporting internal decision making.