Good versus bad fibroblasts
August 17, 2022
Are fibroblasts good or are they bad?
We need to talk about the good and the bad fibroblasts – the dangerous fibroblasts that overgrow organs and destroy organ function, but also the necessary specialized fibroblasts in bone, the osteoblasts.
Fibroblasts are an important type of cell in the human body that play a crucial role in tissue repair and maintenance. However, not all fibroblasts are created equal – there are both good and bad fibroblasts that have vastly different effects on the body.
The dangerous fibroblasts, known as myofibroblasts, are responsible for pathological tissue remodeling in various diseases, such as fibrosis. These fibroblasts overgrow organs and destroy organ function. While myofibroblasts play a role in wound healing, their persistence and unchecked growth can lead to excessive scarring and tissue damage.
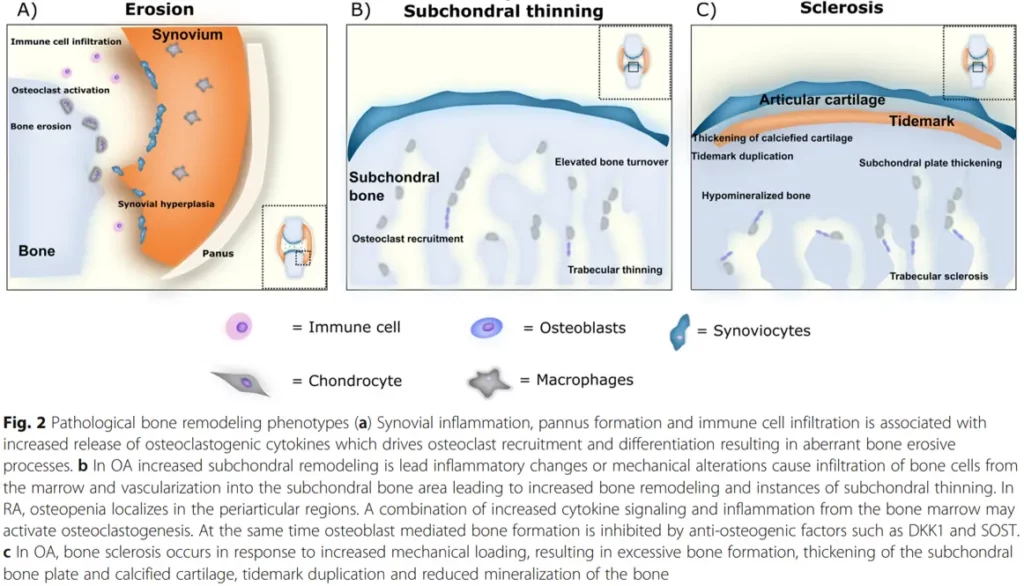
On the other hand, there are specialized fibroblasts, such as osteoblasts, that are necessary for maintaining bone health. Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix that makes up bone tissue, and are crucial in the process of bone formation.
Unfortunately, the success in biomedical sciences such as genomics and proteomics is not paralleled in the medical product development methods, resulting in a lack of translation into improved drug safety and efficacy. This can lead to some antifibrotic treatments having deleterious effects on bone fibroblasts, such as osteoblasts, and may cause unwanted side effects.
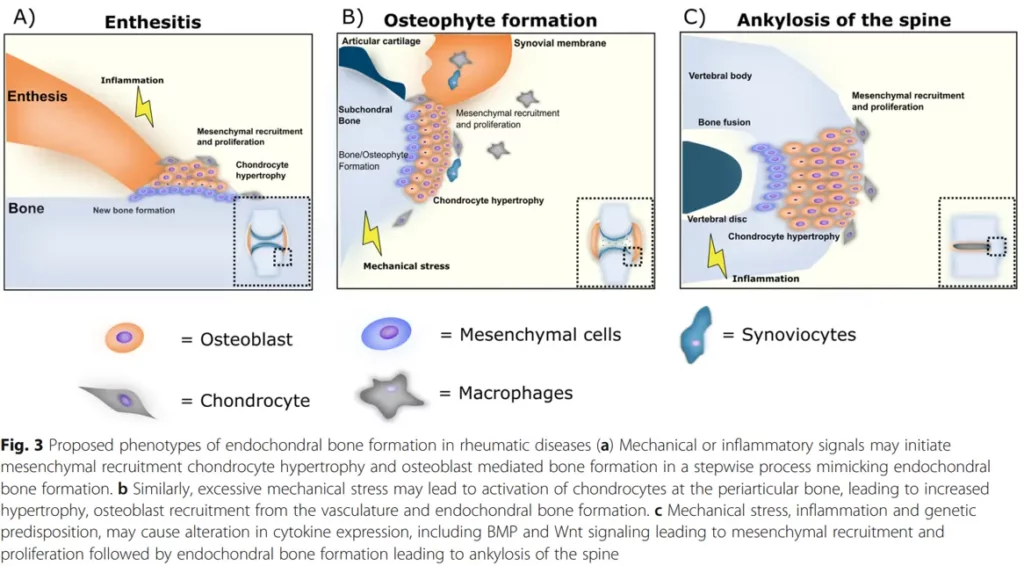
In rheumatic diseases, bone inflammation and remodeling phenotypes are proposed to be a result of endochondral bone formation. Studies have identified bone as a possible endocrine organ, and the availability of valid biochemical bone markers suggests that assessing bone turnover should also play an important role in general safety pharmacology.
To address this issue, there is a need for improved methods to assess the effects of treatments on different types of fibroblasts. This is where bone inflammation panels come in – these panels can be used to assess whether a treatment is having a deleterious effect on bone fibroblasts, such as osteoblasts.
In conclusion, while fibroblasts play a crucial role in tissue repair and maintenance, it is important to distinguish between the good and bad fibroblasts. Unchecked growth of myofibroblasts can lead to tissue damage and organ dysfunction, while osteoblasts are necessary for maintaining bone health. Improved methods of assessing the effects of treatments on different types of fibroblasts, such as bone inflammation panels, can help ensure that treatments are safe and effective.
With our bone inflammation panel, you can assess whether your treatment is having a deleterious effect.
Related publications:
Should biochemical markers of bone turnover be considered standard practice for safety pharmacology?
Biochemical markers in osteoarthritis with lessons learned from osteoporosis
Role of biochemical markers in the management of osteoporosis




